1. Read very carefully, making sure you understand, all the questions and possible answers in the exam.
2. You may underline your answers in the booklet and then read them again before you put them in the answer sheet.
3. Take your time! there is no rush to finish fast.
4. Remember this exam counts for 15% for your evaluation grade.
5. Don't forget you need to bring a Berol-Mirado pencil No. 2.
GUIA DE
ESTUDIO EXAMEN SEP
CIENCIAS
NATURALES
BLOQUE I ¿Cómo mantener la salud?
Prevención de accidentes (23-27)
El sistema digestivo, circulatorio y
excretor (28-37)
Evaluación y autoevaluación (40-41)
BLOQUE II ¿Cómo somos los seres
vivos?
Relación entre los animales y su
ambiente. Clasificación en herbívoros, carnívoros, etc., y en vivíparos,
ovíparos, etc. (cómo nacen) (45-55)
Satisfacción de necesidades básicas
(56-59)
Importancia del cuidado del medio
ambiente (60-67)
Evaluación y autoevaluación (70-71)
BLOQUE III ¿Cómo son los materiales y sus interacciones?
Propiedades de los materiales. Masa
y Volumen. Cambios físicos y cambios químicos. Instrumentos de medición
(balanza, termómetro, regla). (74-93)
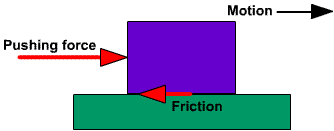
Fuerza, movimiento, fricción.
Evaluación y autoevaluación
(100-101)
BLOQUE IV ¿Qué efectos produce la interacción de las
cosas?
Características de la luz y su
importancia (105-113)
Interacción de imanes y su
aprovechamiento (120-127)
Evaluación y autoevaluación
(128-129)
BLOQUE V ¿Cómo conocemos
Las fases de la luna. Movimientos de
rotación y traslación (132-137)
Evaluación y autoevaluación
(143-144)
Try to do all the evaluations at the end of each Bloque. You can find additional information in the link:
Good luck!















.gif)
